In the ever-evolving landscape of SEO (Search Engine Optimization), strategies like tiered link building have emerged as crucial elements in enhancing a website’s visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs).
Understanding the significance and intricacies of tiered link building is paramount for digital marketers and website owners striving to navigate the complexities of online visibility.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the concept of tiered link building, shedding light on its principles, implementation, and the reasons behind its importance in optimizing a website’s SEO performance.
What is tiered link building?
Before delving into the specifics of link-building techniques, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals. Tiered link building revolves around the concept of establishing backlinks that, in turn, support other backlinks. The primary objective is to enhance the transfer of link authority, commonly referred to as “link juice,” from your collection of backlinks to your primary website.
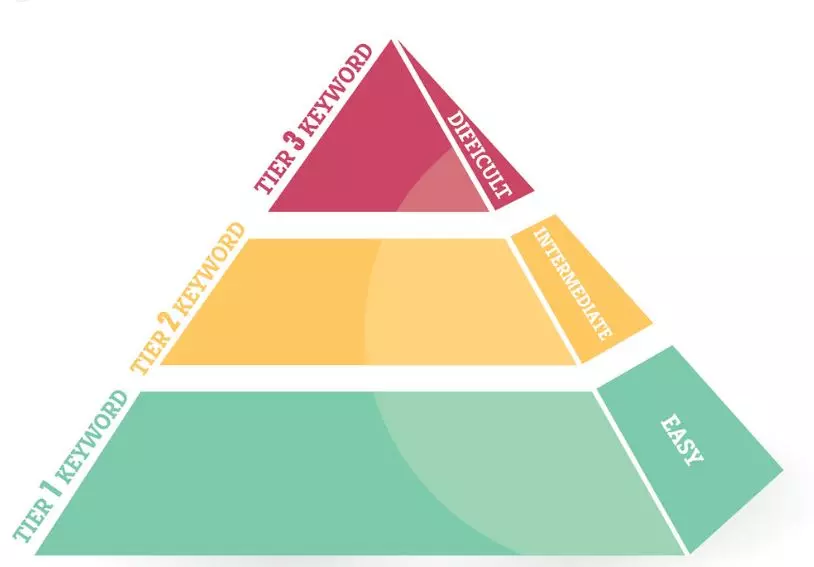
This method involves a hierarchical structure: commencing with tier 1 backlinks directly linked to your main website. Subsequently, tier 2 backlinks are established to point to tier 1 backlinks, followed by tier 3 backlinks directed to each tier 2 link. This tiered link-building method transfers link juice and ranking signals, aiming to strengthen the overall SEO performance of the primary webs
The benefits of tiered link building
1. Improving the quality of tier 1 links
While conventional methods of creating backlinks typically rely on a single-layered approach to generate link equity, tiered link building offers the advantage of leveraging multiple tiers of link equity simultaneously.
This method allows for a gradual transfer of link juice from Tier 3 to Tier 2, followed by Tier 2 to Tier 1, ultimately consolidating the accumulated link equity towards the desired target site.
Tiered link building serves as an efficient strategy to amass link equity from diverse sources without raising suspicions about receiving an excessive number of direct links from multiple websites simultaneously.
Furthermore, building tier 2 links helps to transmit ranking signals for target keywords of the website through tier 1 links. This is a secret strategy that Backlinkita has applied successfully across hundreds of different websites.
Regardless of the chosen structure for tiered link building, the aggregated link authority from this hierarchical approach significantly influences Google’s algorithm to positively evaluate your site’s rankings.
2. Build a safe backlink system
Another advantageous aspect of the tiered link building approach is its ability to establish a robust backlink profile while mitigating the risk of being perceived as a link spammer.
This intricate structure aligns closely with the framework that Google’s algorithms recognize from organic backlinks. Instead of a single layer consisting of numerous referring domains pointing independently to a central destination domain, tiered link building creates a web-like network of interrelated backlinks, both directly and indirectly.
Furthermore, your backlink profile will encompass various types of links, enhancing its diversity. You’ll acquire high-quality backlinks from authoritative webpages, bolstered by a combination of both nofollow and dofollow links.
But it doesn’t stop there. The influence extends deeper, encompassing social media platforms and discussion forums, where social signals validate the relevance of intermediary backlinks.
This strategy ensures your compliance with Google’s guidelines, preventing your website from falling into disfavor. Google’s algorithms are sophisticated enough to swiftly detect and penalize unnatural backlink profiles, making it crucial to maintain a natural and diversified link structure.
3. Minimize the risk of being penalized by Google Penguin
Tiered link building offers the advantage of utilizing a significant volume of lower-quality links while minimizing the associated risks.
For instance, instead of using 1000 links to rank for the keyword “link building services“, when employing tiered link building, your tier 1 links will be of higher authority, and requiring only 500 tier 1 links for ranking for the keyword “link building services.”
Having a smaller number of tier 1 links reduces the risk of your website being penalized by the Google Penguin algorithm.
4. The cost of tier 2, tier 3 link building is cheaper
The impact of second and third-tier backlinks is comparatively weaker than that of your tier 1 backlinks. Since these backlinks aren’t directed straight to your website, any potential violation of Google guidelines by them wouldn’t directly implicate your website.
Building tier 2 or tier 3 links doesn’t require the same level of meticulousness as tier 1 links. Therefore, it helps significantly reduce the cost of backlink building while still yielding maximum effectiveness.
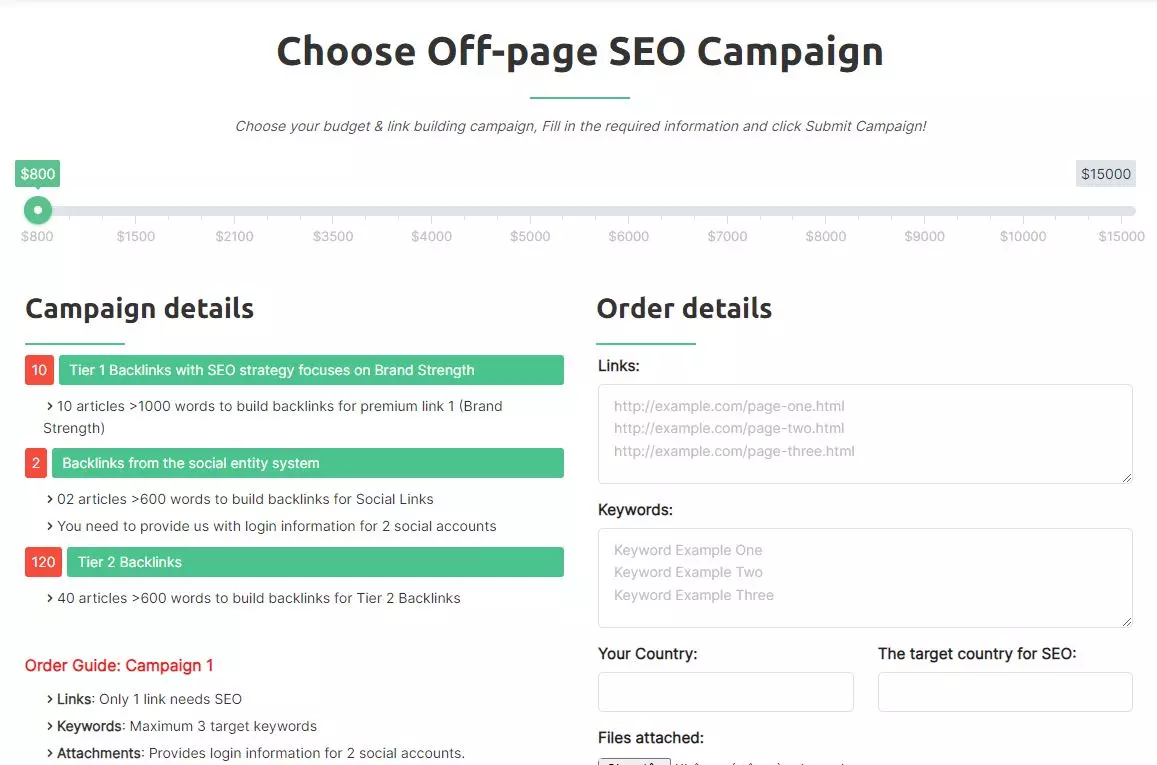
In campaign 1, we built 12 tier 1 backlinks and 120 tier 2 backlinks. The total cost of the campaign was $800 ($800 divided by 12 equals $66.7). Therefore, the cost of building tier 2 links is extremely low; you only need to invest $66.7 to acquire a quality tier 1 backlink (each tier 1 link receives up to 30 tier 2 links).
The risks of tiered link building
Tiered link building falls under the category of gray-hat SEO practices, implying that it inherently involves certain risks:
1. The website was penalized by Google
When Google continues to implement hundreds of algorithm updates annually, its ability to detect quality issues associated with tiered link building has significantly improved. Presently, risking your tiered link building strategy with dubious techniques is a perilous choice, given the potential consequences.
Consider the allure of private blog networks (PBNs) as a quick method for setting up a tier of links. While initially attractive, Google is expected to uncover these schemes in the near future.
Penalties imposed by Google won’t solely target PBN publishers but can extend to those benefiting from these networks.
Another high-risk practice involves the utilization of link building bots such as RankerX or GSA. Although these tools can generate thousands of links, the resulting footprint could make your site vulnerable to Google penalties.
It’s particularly crucial to avoid automated techniques for high-tier backlinks. All links leading to and from your primary referring sites should be meticulously crafted manually.
2. Takes a long time to deploy
Implementing tiered link building on your website can be a time-consuming process. Therefore, the most significant risk here is the potential lack of wise resource investment. Prior to potentially wasting time on tiered link building, it’s advisable to go through an extensive list of SEO strategies that you should consider.
3. High cost
In addition to being time-consuming, tiered link building also exerts a significant strain on marketing resources.
From meticulous planning and content creation to strategic implementation and ongoing monitoring, tiered link building necessitates a comprehensive allocation of resources to yield desired results.
For example, in campaign 1 (as shown in the image above), if you only pay $15 for a tier 1 link, with the construction of 30 tier 2 links pointing to that tier 1 link, you would need to invest an additional $50 to build tier 2 links in order to enhance the quality of the tier 1 link.
How does Google Penguin algorithm impact tiered link-building practices?
The Google Penguin algorithm significantly influences tiered link-building strategies. Introduced to target webspam and manipulative link-building tactics, Penguin specifically penalizes websites employing unnatural, spammy, or low-quality backlinks.
In the context of tiered link building, websites engaging in practices such as acquiring links from irrelevant sources, participating in link schemes, or utilizing automated link-building tools risk being flagged by Penguin.
This algorithm prioritizes organic, high-quality link acquisition, emphasizing the necessity of adhering to Google’s guidelines to avoid penalties and maintain a strong online presence.
Backlinkita’s tiered link building tactics (white hat)
In our link-building strategy, Backlinkita focuses on building links within two tiers: Tier 1 and Tier 2.
The reason we don’t build Tier 3 links is that the ranking signals they convey to the website are very low, so it’s not worth the cost. We have conducted extensive measurements across numerous projects to devise the most optimal approach for our link-building strategy.
How to tier 1 link building
Tier 1 links are direct links to a website, thus posing a higher risk of being penalized by Google Penguin. Therefore, when constructing Tier 1 links, it’s essential to adhere to several quality principles:
- The sources for building Tier 1 links should come from websites that permit link indexing. These domains must have a minimum organic traffic of 1000, minimum organic keywords of 500, and a TF (Trust Flow) metrics > 10.
- Ensure a minimum content length of 1000 words to avoid “Thin Content” issues and to enhance the ranking potential for the keywords associated with each Tier 1 link you create.
- The content used for building backlinks must be directly relevant to the topic cluster of the target keyword to prevent any misinterpretation by Google regarding ranking signals.
How to tier 2 link building
Tier 2 links are links directed towards Tier 1 links rather than directly to the website, thereby posing a lower risk of being penalized by Google Penguin algorithm. Therefore, when constructing Tier 2 links, it’s crucial to adhere to several quality principles:
- The sources for building Tier 2 links should be from websites that allow link indexing and TF score > 5.
- Ensure a minimum content length of 600 words to avoid “Thin Content” issues and to bolster ranking signals to Tier 1 links.
- The content used for constructing backlinks must also be directly relevant to the main topic of the target keyword you aim to rank for, to avoid any misinterpretation by Google regarding ranking signals.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, tiered link building remains a dynamic and influential strategy in modern SEO practices. Its structured approach to link acquisition, emphasizing link equity distribution and authority enhancement, continues to be a cornerstone for improving website rankings and organic traffic.
However, in light of evolving search engine algorithms, especially Google’s scrutiny through algorithms like Penguin, adherence to quality guidelines and the acquisition of high-quality, relevant links have become paramount.
As SEO landscapes evolve, tiered link building stands as a versatile tool when implemented judiciously, contributing significantly to a website’s credibility, visibility, and success in today’s competitive digital realm.